Pea Protein vs Soy vs Rice vs Hemp: The Ultimate Comparison Guide
October 15, 2025

Plant-based proteins are taking center stage in modern nutrition. Whether you are an athlete, a vegan, or simply health-conscious, choosing the right plant protein can be overwhelming. With options like pea protein, soy protein, rice protein, and hemp protein, how do you decide which one suits your body best?
In this guide, we’ll break down their nutritional profiles, digestibility, allergen concerns, and functional benefits so you can make an informed choice. Welcome to Pea Protein vs Soy vs Rice vs Hemp: The Ultimate Comparison Guide.
Why Plant Proteins Matter
As more consumers seek allergen-free plant protein options, traditional animal-based sources are being replaced with sustainable, plant-derived alternatives. Beyond sustainability, plant proteins provide fiber, phytonutrients, and lower saturated fat levels. Choosing wisely between pea, soy, rice, and hemp protein means understanding their amino acid profiles, digestibility scores, and potential health impacts.

Pea Protein
Nutritional Profile
Pea protein, derived from yellow split peas, has become a top choice for functional plant protein ingredients. It is naturally rich in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) that support muscle repair and growth.
- High in lysine (an essential amino acid often lacking in other plant proteins)
- Moderate levels of methionine and cysteine
- Often marketed as pea protein isolate, with protein content of 80–85%
Digestibility
Pea protein boasts a digestibility score of around 0.82–0.93, making it highly bioavailable compared to other plant proteins.
Benefits
- Hypoallergenic protein – free from common allergens like soy, gluten, and dairy
- Smooth texture in shakes, making it a leading option for the best plant protein for shakes
- Supports athletes seeking a clean, sustainable protein source

Soy Protein
Nutritional Profile
Soy protein is one of the most researched plant proteins. It’s considered a complete amino acid plant protein, similar to whey.
- High levels of glutamine and arginine
- Available as soy protein concentrate or soy protein isolate (≥90% protein)
Digestibility
Soy protein has a Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) of 1.0, the highest possible, making it one of the most digestible plant proteins.
Benefits
- Proven muscle-building support
- Heart health benefits through cholesterol reduction
- Affordable and widely available
Concerns
- Some consumers avoid soy due to concerns about phytoestrogens
- Common allergen, making soy protein isolate vs pea protein isolate a key consideration for sensitive individuals

Rice Protein
Nutritional Profile
Brown rice protein is naturally gluten-free and easy to digest. However, it lacks sufficient lysine compared to pea protein.
- Rich in cysteine and methionine
- Often blended with pea protein to create a complete amino acid profile
Digestibility
Rice protein offers good digestibility, though slightly lower than soy and pea.
Benefits
- Ideal for those with food sensitivities
- Gentle on digestion, making it popular for rice protein vs pea protein digestion discussions
- Clean flavor profile suitable for shakes and bars

Hemp Protein
Nutritional Profile
Hemp protein is made from ground hemp seeds. While not as protein-dense as isolates, it contains additional nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and minerals.
- Balanced amino acid profile, though slightly lower in lysine
- Typically 50% protein content, higher in whole-food nutrition value
Digestibility
Hemp protein has moderate digestibility but excels in overall gut health benefits due to its fiber content.
Benefits
- Naturally rich in essential fatty acids
- Supports overall wellness, not just muscle building
- Appeals to the plant protein for athletes market seeking nutrient diversity
Key Comparison: Pea vs Soy vs Rice vs Hemp
When it comes to choosing the right plant-based protein, no single option fits all. Each source — pea, soy, rice, and hemp — comes with its own strengths and limitations. Understanding how they compare side by side helps consumers, athletes, and product developers decide which ingredient best matches their nutritional and functional needs.
Below is a simplified comparison across four major criteria: amino acid balance, digestibility, allergen concerns, and practical applications.
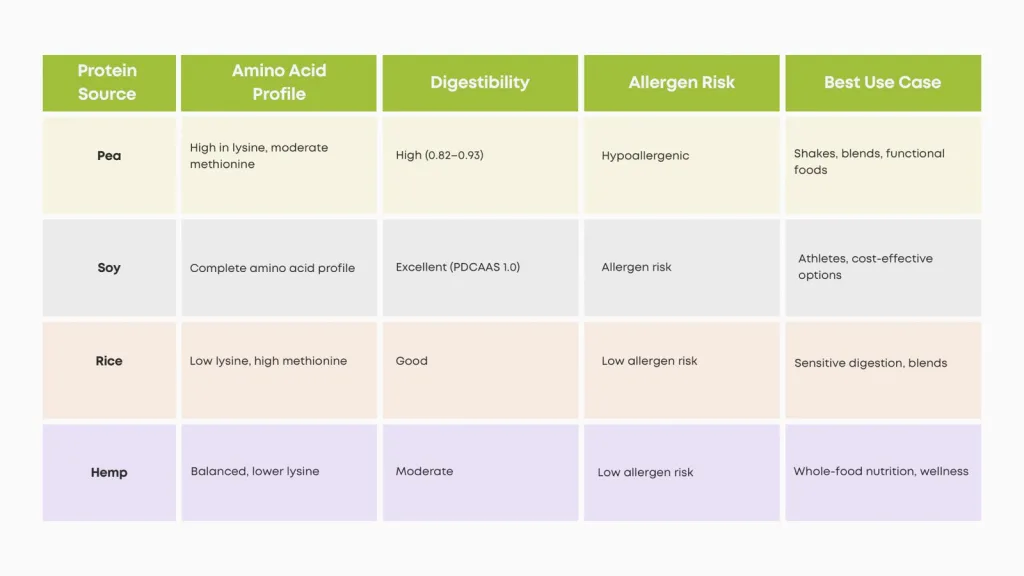
Which Protein Should You Choose?
When comparing pea protein vs soy vs rice vs hemp, the right choice depends on your goals:
- For muscle growth: Soy protein or pea protein isolate
- For sensitive digestion: Rice protein or hemp protein
- For allergen-free nutrition: Pea protein and hemp protein
- For complete amino acid plant protein: Soy, or pea + rice blend
By considering amino acid profiles, digestibility, and allergen concerns, you can identify the best plant protein for shakes, bars, or functional foods tailored to your needs.
Functional Applications in Food & Beverages
Many brands now incorporate functional plant protein ingredients into their product lines:
- Pea protein: Dairy alternatives, protein shakes, meat substitutes
- Soy protein: Nutrition bars, sports supplements, fortified cereals
- Rice protein: Sensitive-digestion formulas, baby food, allergen-free snacks
- Hemp protein: Smoothies, wellness powders, holistic nutrition products
This versatility makes them highly valuable in today’s health-conscious marketplace.
Choosing Your Ultimate Plant Protein
When it comes to Pea Protein vs Soy vs Rice vs Hemp: The Ultimate Comparison Guide, there is no single winner. Each protein source offers unique benefits for different dietary needs and lifestyles.
For individuals or brands seeking hypoallergenic protein with strong digestibility, pea protein is an excellent option. For complete amino acid coverage, soy remains reliable, while rice and hemp proteins provide added diversity and digestive support.
Discover Functional Plant Protein Solutions with Satoria Nutrisentials
At Satoria Nutrisentials, we specialize in functional plant protein ingredients designed for modern food and beverage innovations. Whether your brand needs pea protein, resistant dextrin, or other specialized ingredients, we provide solutions that combine science, nutrition, and market appeal.
Ready to explore the future of plant-based nutrition?
Contact us today and learn how our premium ingredients can power your next product innovation.
References
- Friedman, M., & Brandon, D. L. (2001). Nutritional and health benefits of soy proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49(3), 1069–1086.
- Gorissen, S. H., Crombag, J. J., Senden, J. M., Waterval, W. A., Bierau, J., & van Loon, L. J. (2016). Protein content and amino acid composition of commercially available plant-based protein isolates. Amino Acids, 48(12), 1–12.
- Hughes, G. J., Ryan, D. J., Mukherjea, R., & Schasteen, C. S. (2011). Protein digestibility-corrected amino acid scores (PDCAAS) for soy protein isolates and concentrate: criteria for evaluation. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(23), 12707–12712.
- Tang, J. E., Moore, D. R., Kujbida, G. W., Tarnopolsky, M. A., & Phillips, S. M. (2009). Ingestion of whey hydrolysate, casein, or soy protein isolate: Effects on mixed muscle protein synthesis. Journal of Applied Physiology, 107(3), 987–992.
- Wang, Q., & Xiong, Y. L. (2016). Processing, nutrition, and functionality of hempseed protein: A review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 15(3), 549–567.