Maltodextrin in Food: What B2B Manufacturers Need to Know for Modern Formulations
January 15, 2026

Maltodextrin in food has been a widely used ingredient for decades, particularly valued for its versatility in processing, bulking, stabilization, and energy release. As the global food and beverage industry continues to shift toward clean-label expectations, healthier formulations, and functional ingredients, manufacturers are reassessing how maltodextrin fits into modern product development. For some applications, maltodextrin remains an efficient solution. However, in many cases, the industry is seeing a growing preference for cleaner alternatives with improved nutritional benefits—particularly resistant dextrin, functional fibers, and plant-based enhancers.
For B2B manufacturers, understanding the evolving role of maltodextrin in food is essential for meeting both regulatory expectations and shifting consumer demands. This article explores the benefits and limitations of maltodextrin, how it performs in different product categories, and why many manufacturers are transitioning to better-for-you replacements—like the solutions offered by Satoria NutriSentials, including resistant dextrin, functional fiber systems, and pea protein.
Throughout this article, we will cover the latest insights, technical considerations, clean-label alternatives, and how ingredient innovation can help you future-proof your formulations in a competitive market.
Understanding Maltodextrin in Food Formulation
Maltodextrin is a polysaccharide derived from starch—commonly corn, tapioca, rice, potato, or wheat—through a process called partial hydrolysis. It is classified based on its DE (dextrose equivalent), which indicates the degree of hydrolysis and resulting sweetness level. The higher the DE value, the sweeter the maltodextrin will be.
Because maltodextrin is neutral in flavor and highly soluble, it is frequently used in both dry and liquid formulations. Its popularity among manufacturers stems from its functional versatility, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with a wide range of applications.
Despite its widespread use, consumer awareness about added carbohydrates and processed ingredients is changing how food developers evaluate maltodextrin. Many product categories are now shifting toward natural, low-GI, or dietary fiber–based bulking agents. As a result, understanding maltodextrin’s performance characteristics—and its limitations—has become critical in product reformulation.
Key Functional Roles of Maltodextrin in Food Manufacturing
Maltodextrin delivers several functional benefits that make it attractive to manufacturers. These technical roles help maintain consistency, structure, mouthfeel, and product stability.
1. Bulking and texture enhancement
Maltodextrin adds volume without contributing excessive sweetness. This makes it ideal for:
- Powdered drink mixes
- Instant soups and sauces
- Snack seasonings
- Confectionery products
- Nutritional supplements
It provides body and smoothness, helping manufacturers achieve the desired sensory profile.
2. Stabilization and binding
In sauces, dairy products, plant-based drinks, and frozen treats, maltodextrin functions as a binder and stabilizer. It supports emulsification and can help slow crystallization, especially in frozen desserts.
3. Improved mouthfeel
Maltodextrin contributes to creaminess and reduces grittiness in beverages, powders, and protein blends. However, modern alternatives—especially resistant dextrin and prebiotic fibers—offer similar or improved mouthfeel with added functional benefits.
4. Carrier for flavors and active ingredients
In spray-drying and encapsulation, maltodextrin acts as a carrier by protecting sensitive compounds such as:
- Natural flavors
- Vitamins
- Essential oils
- Sweeteners
This improves stability, shelf life, and dispersibility.
5. Energy source in sports nutrition
Maltodextrin is rapidly absorbed, making it a common carbohydrate source for athletic gels, drinks, and energy powders. However, the demand is shifting toward low-GI, slower-digesting carbohydrates and fiber-based solutions for more sustained energy release.
Limitations of Maltodextrin in Modern Food Technologies
While maltodextrin offers attractive processing benefits, several limitations are driving manufacturers to explore cleaner alternatives.
1. High glycemic index (GI)
Maltodextrin has a glycemic index close to glucose, which can spike blood sugar levels. As consumers become more health-conscious, high-GI ingredients are increasingly scrutinized. Brands developing “low sugar,” “reduced carb,” or “diabetic-friendly” products find maltodextrin incompatible with their positioning.

2. Regulatory and clean-label concerns
Although maltodextrin is generally recognized as safe (GRAS), many consumers perceive it as overly processed due to:
- Chemical-sounding name
- Association with artificial additives
- Lack of nutritional contribution
This perception conflicts with clean-label trends.

3. Lack of dietary fiber
Maltodextrin contributes calories but no fiber or functional health benefits, making it less aligned with current market demands for:
- Gut health support
- Prebiotic benefits
- Satiety enhancement
- Low-GI formulations
Modern alternatives like resistant dextrin provide these benefits while maintaining similar functionality.

4. Not ideal for plant-based positioning
As plant-based beverages, snacks, and supplements grow, consumers prefer functional ingredients that provide nutritional value. Maltodextrin’s role is primarily technical rather than nutritional.
Why Many Manufacturers Are Transitioning to Cleaner Alternatives
The shift away from maltodextrin in food is not driven by performance issues alone. The change is happening because modern consumers demand transparency, health benefits, and natural-sounding ingredients.
Market trends influencing the shift include:
- Rising demand for functional fibers
- Increased awareness of blood sugar response
- Preference for low-GI carbohydrate sources
- Regulatory shifts toward clearer labeling
- Growth of prebiotic and gut-health positioning
As a result, resistant dextrin and other functional fibers are becoming the preferred replacements. Brands can maintain or improve texture and stability while elevating nutritional claims and clean-label appeal.
Comparing Maltodextrin vs. Resistant Dextrin: Technical and Nutritional Differences
Resistant dextrin—one of Satoria NutriSentials’ flagship ingredients—is often used as a more functional and health-forward alternative to maltodextrin. Both ingredients share similar solubility and processing advantages, but the similarities end there.
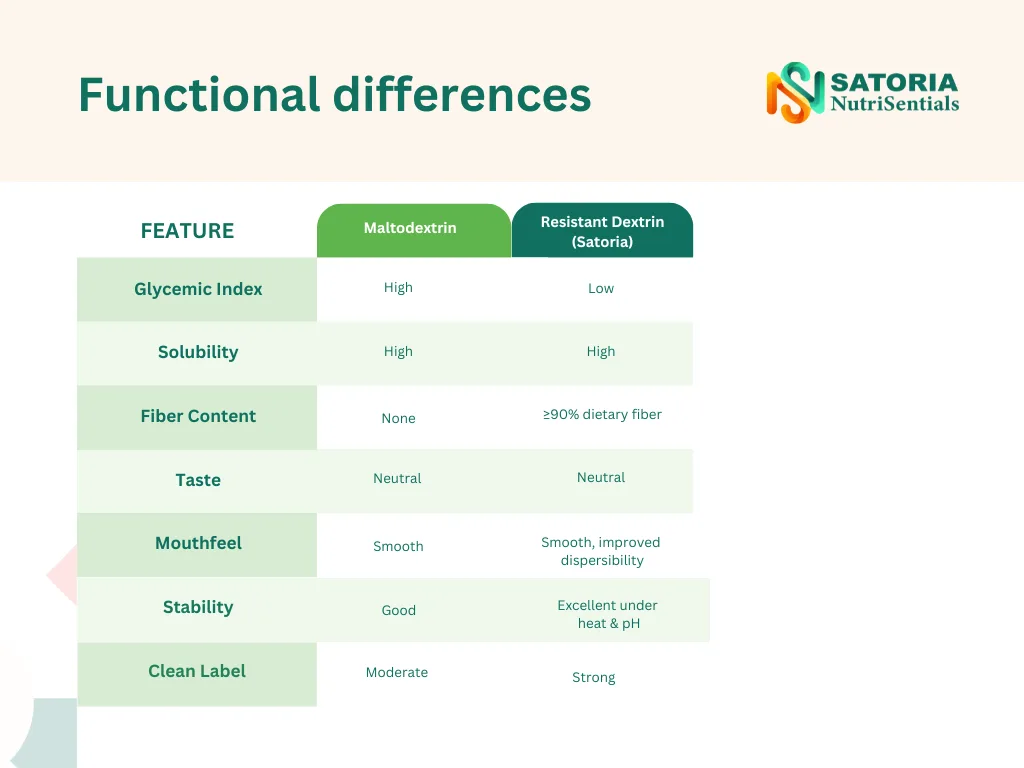
Nutritional impact differences
Maltodextrin spikes blood sugar, provides empty calories, and contributes no functional health benefits. Resistant dextrin, in contrast, offers:
- Prebiotic effects
- Improved digestive health
- Better satiety
- Lower calorie contribution
- Enhanced nutrient absorption support
For manufacturers developing health-oriented products, resistant dextrin creates significant formulation and marketing advantages.
Applications Where Resistant Dextrin Outperforms Maltodextrin
Satoria NutriSentials’ resistant dextrin can replace maltodextrin in multiple categories without compromising performance. In many cases, it enhances product quality.
1. Beverages and powdered drinks
Resistant dextrin disperses instantly and remains clear when dissolved, avoiding cloudiness. It is ideal for:
- Electrolyte beverages
- Functional waters
- Fiber-enriched juices
- Coffee mixes
- Milk alternatives
Its low viscosity allows high inclusion rates without altering texture.
2. Sports and performance nutrition
Instead of fast-absorbing carbs, consumers increasingly prefer slow-release or balanced-energy sources. Resistant dextrin supports:
- Sustained energy
- Gut comfort during exercise
- Better blood glucose management
It is suitable for pre-, intra-, and post-workout formulations.
3. Bakery and snacks
Where maltodextrin adds bulk, resistant dextrin adds bulk plus improved:
- Crispiness in extruded snacks
- Moisture retention in baked goods
- Shelf-life stability
Its low sweetness allows formulation flexibility.
4. Supplements and meal replacements
Resistant dextrin pairs well with Satoria’s plant-based proteins—particularly pea protein and pea protein isolate. This combination enhances texture, dispersibility, and nutritional fortification.
How Satoria NutriSentials Supports the Shift Beyond Maltodextrin
Satoria NutriSentials provides a portfolio of high-quality functional ingredients designed for modern, health-forward formulations. Their key offerings include:
Resistant Dextrin (featured alternative to maltodextrin)
A clean-label, highly soluble fiber ideal for beverages, snacks, supplements, and sports nutrition.
Pea Protein & Pea Protein Isolate
Plant-based proteins that improve texture, mouthfeel, and amino acid profile for functional beverages and food systems.
SweetSentials™ (Natural Sweetener Solutions)
Reduced-calorie, low-GI sweeteners that integrate well with resistant dextrin for balanced sweetness and fiber enhancement.
Other Functional Fiber Systems
Tailored solutions to boost digestive health, reduce sugar content, and improve overall formulation performance.
All products are backed by technical support, R&D guidance, and application testing to help manufacturers transition smoothly from maltodextrin-based formulations to modern alternatives.
Best Practices for Replacing Maltodextrin in Formulation Development
When developing or reformulating products, B2B brands must evaluate several technical factors. Below are recommended steps for a smooth transition.
1. Evaluate desired sensory properties
Assess sweetness, texture, and mouthfeel requirements.
2. Conduct solubility and dispersibility tests
Resistant dextrin typically blends seamlessly but should be tested according to your manufacturing process.
3. Adjust viscosity and bulking levels
Because resistant dextrin has lower viscosity, inclusion rates may differ from maltodextrin.
4. Consider nutritional positioning
Replacing maltodextrin enables claims such as:
- “High fiber”
- “Digestive support”
- “Low GI”
- “Supports gut health”
5. Validate stability across pH and temperature
Satoria’s resistant dextrin delivers strong stability in acidic beverages and thermal processing.
Formulation Case Examples for B2B Manufacturers
Functional Beverage Prototype
- 3% resistant dextrin
- 2% SweetSentials™ natural sweetener
- Plant extract + flavor system
- Clear, stable, fiber-enriched drink
Protein Shake Blend
- 65% pea protein
- 25% resistant dextrin
- 5% cocoa or flavor
- 5% sweetener + stabilizer
Improved dispersibility, reduced grittiness, and cleaner label appeal.
High-Fiber Snack Extrudate
- Improved crisp structure
- Enhanced expansion
- Better moisture control
The Future of Maltodextrin in Food Manufacturing
Maltodextrin will continue to serve certain applications where cost or rapid carbohydrate delivery is required. However, the broader market trend is clear: manufacturers must incorporate better-for-you carbohydrates and functional fibers to stay competitive.
Resistant dextrin and other fiber-based alternatives will dominate the next generation of:
- Functional beverages
- Health snacks
- Sports nutrition
- Meal replacements
- Plant-based formulations
B2B manufacturers embracing cleaner, smarter ingredients today will be positioned for long-term success.
Partner with Satoria NutriSentials for Modern Ingredient Solutions
If your brand is exploring how to reduce maltodextrin, enhance nutritional value, or optimize clean-label formulations, Satoria NutriSentials can support you through:
- Ingredient selection
- Application testing
- Technical formulation support
- Regulatory guidance
- Tailored product development
Their portfolio of resistant dextrin, plant-based proteins, and natural sweeteners provides a complete toolkit for manufacturers building the next generation of health-driven products.
Reference
- Cummings, J. H., & Stephen, A. M. (2007). Carbohydrate terminology and classification. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 61(S1), S5–S18.
https://www.nature.com/articles/1602936 - Food and Drug Administration. (2023). GRAS Notices—Maltodextrin. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
https://www.fda.gov/food/generally-recognized-safe-gras/gras-notice-inventory - Gibson, G. R., Hutkins, R., et al. (2017). The role of prebiotics in health. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 14(8), 491–502. https://www.nature.com/articles/nrgastro.2017.75
- International Food Information Council. (2023). Understanding carbohydrates in food production. https://foodinsight.org/carbohydrates-food-production/
https://foodinsight.org/carbohydrates-food-production/ - Slavin, J. (2013). Fiber and prebiotics: Mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients, 5(4), 1417–1435. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3705355/